
Intelligent spam protection for TYPO3 forms without CAPTCHA – AI-based solution with n8n
Do you know that feeling? As soon as you publish a new contact form on your company website, hordes of bots descend upon it and flood your inbox with automated requests. In the past, this was at least somewhat entertaining. There were the occasional generous inheritances from Nigerian princes waiting to be paid out. Or unsolicited offers related to men's health. 😉 I'm sure each of us can picture the appropriate spam email from our own experience. Nowadays, however, spammers don't even bother with that anymore. Instead, we now even receive form submissions with randomly generated character strings.
What we as agency professionals tend to shrug off and respond to with the familiar trio of “seen, laughed, deleted” can become a real problem for our customers. Because—apart from these obvious cases—not everyone can immediately tell when a request is genuine and valid and when it is not. Otherwise, phishing, social engineering, and CEO fraud, for example, would not be nearly as successful. Especially with touchpoints that are as highly exposed as the aforementioned form pages, it is important to separate the wheat from the chaff and ward off unwanted inquiries as much as possible.

Why traditional spam protection mechanisms are reaching their limits
The TYPO3 form framework itself only offers basic spam protection, such as honeypot fields. The conventional remedy for public forms is therefore CAPTCHAs (computer automated public Turing test to tell computers and humans apart). However, these pose a considerable hurdle for the desired human user, because the letter sequences displayed are often really difficult for humans to decipher. For this reason, systems were later developed that provided a spoken version of the letter sequence in parallel, which could then be typed in. Grotesquely, these audio CAPTCHAs made it easier for bots to pass the test as well. Obviously, it is also easier for machines to understand speech than to recognize image patterns. Since websites are increasingly required to be accessible, CAPTCHAs have become a real problem because they can practically never be implemented in an accessible way.
However, the fundamental problem with using CAPTCHAs is that they only address the symptoms. The initial problem was that we wanted to know which requests were legitimate and which were obviously spam. As it turns out, this question has become much easier to answer thanks to the availability of AI and powerful language models. Instead of a CAPTCHA, which effectively interferes with the user's experience when using a form and negatively affects its conversion rate, we now analyze the submitted form data and let the LLM decide whether a request should be forwarded or rejected.
AI-based spam protection: The modern alternative to CAPTCHA
The technical basis for our spam protection is the n8n process automation system from Berlin-based n8n GmbH. As a TYPO3 agency, we developed this solution specifically for enterprise customers who require both the highest security standards and an optimal user experience. n8n offers the ability to link different data sources in an event-driven manner, evaluate data, make decisions, and then trigger various actions. n8n can be operated as a Docker container on one's own infrastructure. It can use any OpenAI-compatible LLM for its AI-related tasks. Together with LLM hosting from mittwald, this creates a completely data-sovereign platform that is operated in Germany, offering us a wide range of options for processing personal data in compliance with the GDPR. For companies that process sensitive customer data, this is a decisive advantage over cloud-based solutions from US providers.
TYPO3 integration: Seamless connection via webhooks
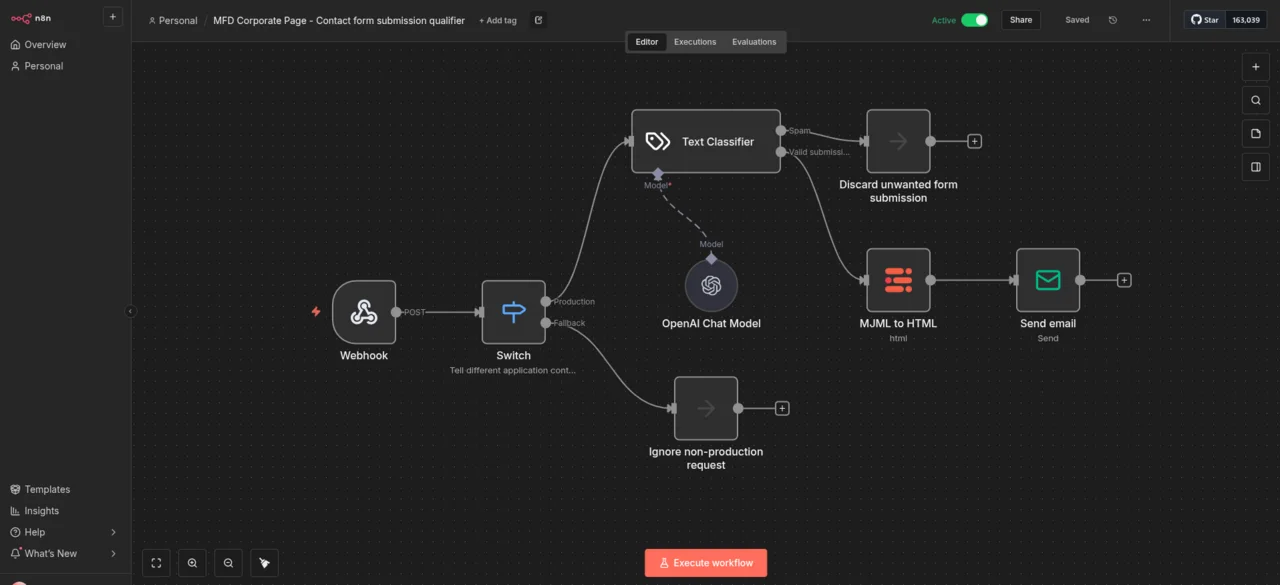
n8n can both periodically query external systems itself and be triggered externally via HTTP webhook. With the t3brightside/formwebhooksend extension, we have enabled the TYPO3 form framework to transmit submitted form data to n8n via such a webhook. As soon as a form is submitted, TYPO3 calls the webhook provided by n8n and transmits a JSON object with the form data. This object also contains additional information that can be stored in the form configuration. This allows you to specify, for example, which form was submitted from which page or where the classified data should be forwarded to. Finally, we also receive information about the application context of TYPO3, which allows us to discard requests from test systems altogether.
Configuring the webhook is very simple:
finishers:
-
options:
webhookUrl: '%env(WEBHOOK_CONTACT_FORM_SUBMISSION)%'
apiToken: 'yourpassword'
customValues: |
recipientAddress: info@marketing-factory.de
subject: Neue Anfrage über die Website
fieldMappings: ''
identifier: FormwebhooksendFinisherThe process can then be created in n8n using the graphical editor. n8n provides a URL for the webhook trigger, which must be entered as webhookUrl in the above configuration. The process may look like this:
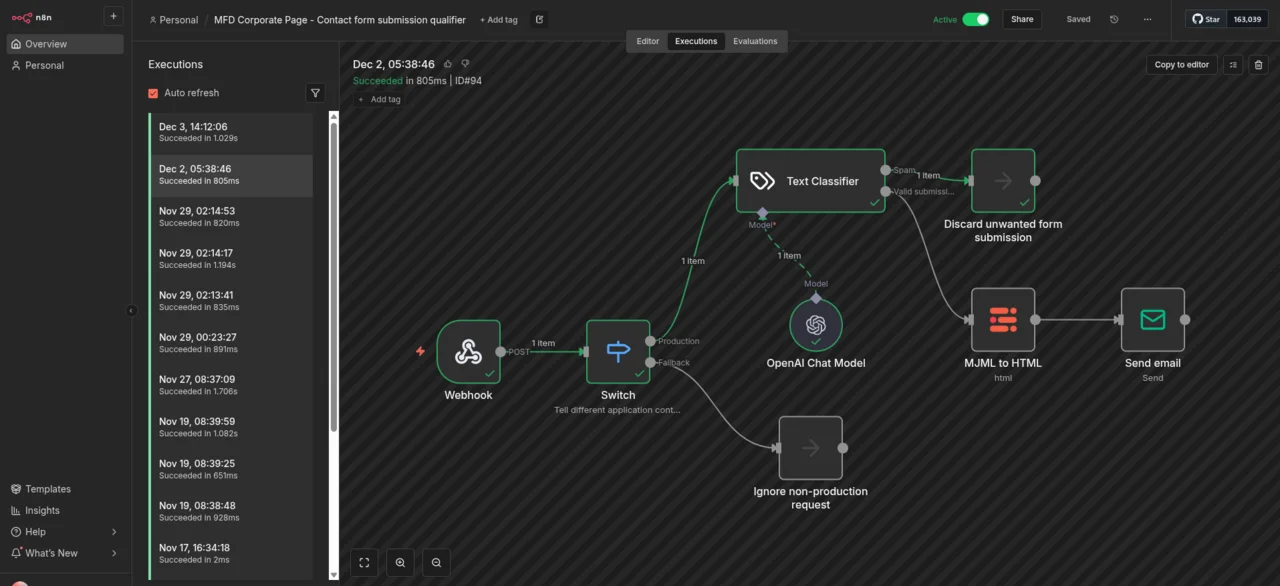
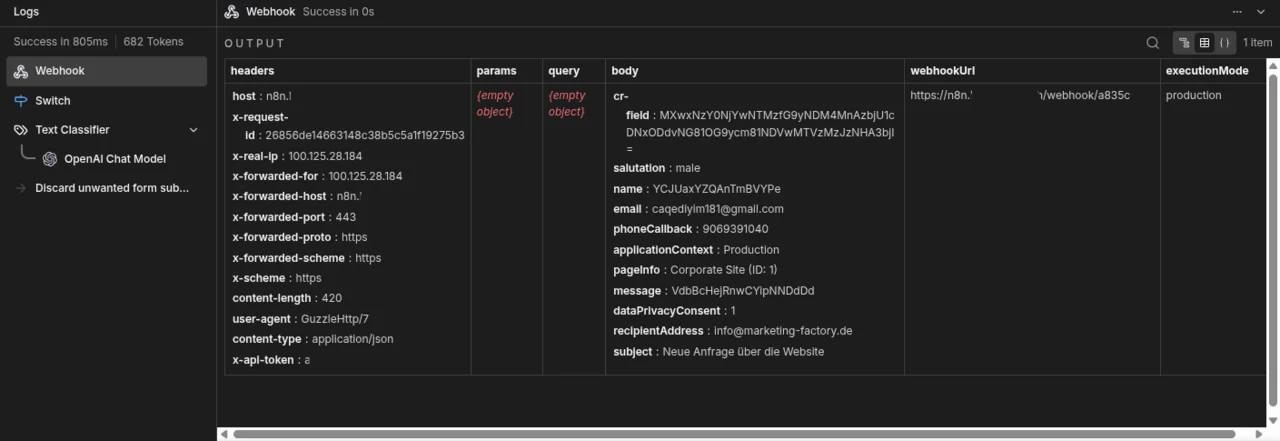
Intelligent classification: How AI distinguishes spam from genuine requests
The incoming data is first filtered according to the respective context (development, production, etc.). Only data from the production system is processed further. The JSON data then runs into a text classifier. This sends it together with a corresponding prompt to an OpenAI-compatible model—in this case, the gpt-oss-120b model provided by mittwald. The task is very simple: all requests that contain offensive language or are obviously undesirable, e.g., because they contain the aforementioned random character strings, are sorted out. What remains are exactly the requests we want to keep, and these are currently forwarded in the form of an email. This AI-supported spam detection achieves a hit rate of over 99% and eliminates both obvious random strings and more elaborate attempts that would bypass conventional filters.
The use of n8n offers us the opportunity to run the data into a CRM instead of sending it by email without making any changes to TYPO3. In addition, the workflows performed, including their data and decision paths, can be visualized very well retrospectively and thus checked for correct functioning. This also provides excellent insights in customer projects where data is transferred to third-party systems and enables targeted error analysis.
For our customers, this intelligent spam protection offers concrete business advantages: no more missed genuine inquiries due to overflowing mailboxes, significantly reduced effort in manually reviewing form entries, and a higher conversion rate by eliminating annoying CAPTCHAs. At the same time, the solution with German hosting ensures full GDPR compliance—a decisive advantage for companies that process sensitive customer data. As long-standing TYPO3 experts, we seamlessly implement such automation solutions into existing systems and ensure continuous optimization of our customers' digital touchpoints.
Please feel free to share this article.
Comments
No comments yet.